Optimization
This section shows how to optimize hyperparameters of covariance functions in Ariadne. The package currently implements two methods:
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm for sampling from the posterior. This method requires specifying a prior distribution for each hyperparameter.
Simple gradient descent algorithm. The implementation includes only a very basic form of gradient descent.
Metropolis-Hastings algorithm
The Metropolis-Hastings algorithm is a simple Monte Carlo method for sampling from the posterior distribution. Let \(\theta\) represent hyperparameters of a covariance function. Then the posterior distribution is defined as
\[p(\theta \mid X, Y) \propto p(Y \mid X, \theta) p(\theta)\]
where \(X\) are locations of observations and \(Y\) are the observed function values. Then \(p(Y \mid X, \theta)\) is the Gaussian process likelihood of observed data.
To be able to sample from the posterior distribution, first we need to specify a prior distribution over hyperparameters \(p(\theta)\). For the squared covariance function, hyperparameters are the lengthscale \(l\), signal variance \(\sigma^2\) and noise variance \(\sigma^2_{\text{noise}}\).
\[\theta = \left( l, \sigma^2, \sigma^2_{\text{noise}} \right)\]
Specifying prior distribution
Because the hyperparameters must be positive, we will use a simple log-normal prior distribution for each hyperparameter.
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: |
#r "Ariadne.dll" open Ariadne.GaussianProcess open Ariadne.Kernels #r "MathNet.Numerics.dll" open MathNet.Numerics let rnd = System.Random(3) let lengthscalePrior = Distributions.LogNormal.WithMeanVariance(2.0, 4.0, rnd) let variancePrior = Distributions.LogNormal.WithMeanVariance(1.0, 5.0, rnd) let noisePrior = Distributions.LogNormal.WithMeanVariance(0.5, 1.0, rnd) |
Ariadne includes a simplified method to work with squared exponential kernels. We can define a prior distribution over squared covariance hyperparameters and directly sample squared covariance kernels from it.
1: 2: 3: |
let prior = SquaredExp.Prior(lengthscalePrior, variancePrior, noisePrior) let kernel = prior.Sample() let gp = kernel.GaussianProcess() |
Now that we specified a prior distribution, we can use Metropolis-Hastings algorithm to get samples from the posterior distribution of hyperparameters given training data.
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: |
// Optimization open Ariadne.Optimization let data = [{Locations = (...) Observations = (...) }] |
To sample from the posterior distribution with squared exponential kernel, we can
use a built-in function optimizeMetropolis. This function runs Metropolis-Hastings
algorithm with symmetric proposal distribution, i.e. basic Metropolis algorithm.
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: 12: 13: 14: 15: 16: |
// Metropolis sampling for squared exponential with default settings let newKernel1 = kernel |> SquaredExp.optimizeMetropolis data MetropolisHastings.defaultSettings prior // Specify custom parameters open Ariadne.Optimization.MetropolisHastings let settings = { Burnin = 500 // Number of burn-in iterations Lag = 5 // Thinning of posterior samples SampleSize = 100 } // Number of thinned posterior samples let newKernel2 = kernel |> SquaredExp.optimizeMetropolis data settings prior |
The Metropolis sampler takes a specified total number of samples, 50 by default, and returns the posterior mean estimate for each hyperparameter.
Squared exponential, l = 0.52, σ² = 22.41, σ²_{noise} = 0.26
We can compare difference in fit of the randomly sampled covariance parameters kernel
and sampled values in newKernel2. You might need to re-run the sampler for more iterations
or with a different starting location to arrive to a good posterior estimate of hyperparameter
values. Note that each iteration of the Metropolis-Hastings sampler has \(\mathcal{O}(N^3)\)
time complexity.
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: |
let gpInit = kernel.GaussianProcess() let gpOptim = newKernel2.GaussianProcess() let loglikInit = gpInit.LogLikelihood data let loglikOptim = gpOptim.LogLikelihood data printfn "Initial log likelihood: %f \nFinal log likelihood: %f" loglikInit loglikOptim |
Initial log likelihood: -231.973587
Final log likelihood: -41.512115
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: |
open FSharp.Charting kernel.GaussianProcess() |> plot data |> Chart.WithTitle("Randomly sampled kernel", InsideArea=false) |> Chart.WithMargin(0.0,10.0,0.0,0.0) |
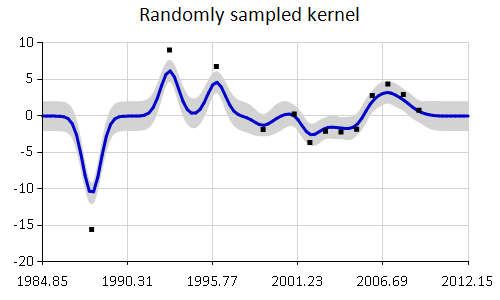
1: 2: 3: |
newKernel2.GaussianProcess() |> plot data |> Chart.WithTitle("Optimized kernel (MH)", InsideArea=false) |> Chart.WithMargin(0.0,10.0,0.0,0.0) |
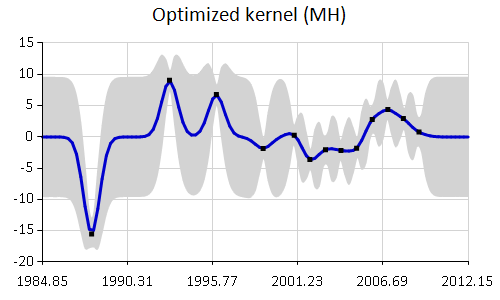
Running general Metropolis-Hastings
It is also possible to run general Metropolis-Hastings algorithm to obtain samples
from the posterior distribution by calling sampleMetropolisHastings function.
The function operates over an array of parameter values. As parameters, it takes functions that
compute log likelihood, transition probability, Markov Chain settings and a proposal
sampler. See the source code for details.
Gradient descent algorithm
It is also possible to fit hyperparameters of covariance functions using any gradient-based optimization algorithm. Ariadne currently implements only basic gradient descent.
The gradientDescent function operates over an array of parameter values.
It requires a function that computes gradient
of log likelihood with respect to all hyperparameters. There is an implementation
of gradient for squared exponential covariance kernel. Because there are local maxima
in the likelihood function, gradient descent might require several restarts with different
initial locations and step sizes.
1: 2: 3: 4: 5: 6: 7: 8: 9: 10: 11: 12: 13: 14: |
// Gradient descent settings let gdSettings = { GradientDescent.Iterations = 10000; GradientDescent.StepSize = 0.01} let gradientFunction parameters = SquaredExp.fullGradient data parameters // Run gradient descent let kernelGD = gradientDescent gradientFunction gdSettings (kernel.Parameters) |> SquaredExp.ofParameters let gpGD = kernelGD.GaussianProcess() printfn "Original Gaussian process likelihood: %f" (gpInit.LogLikelihood data) printfn "Optimized Gaussian process likelihood: %f" (gpGD.LogLikelihood data) |
Original Gaussian process likelihood: -231.973587
Optimized Gaussian process likelihood: -37.614942
1: 2: 3: |
gpGD |> plot data |> Chart.WithTitle("Optimized kernel (GD)", InsideArea=false) |> Chart.WithMargin(0.0,10.0,0.0,0.0) |
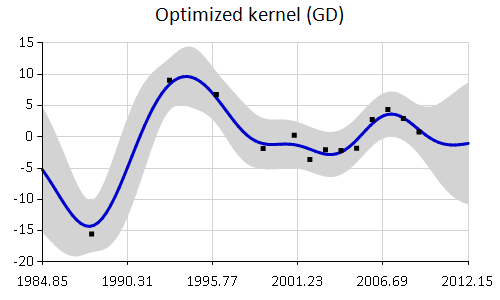
from Ariadne
from Ariadne
Full name: Optimization.rnd
type Random =
new : unit -> Random + 1 overload
member Next : unit -> int + 2 overloads
member NextBytes : buffer:byte[] -> unit
member NextDouble : unit -> float
Full name: System.Random
--------------------
System.Random() : unit
System.Random(Seed: int) : unit
Full name: Optimization.lengthscalePrior
type LogNormal =
new : mu:float * sigma:float -> LogNormal + 1 overload
member CumulativeDistribution : x:float -> float
member Density : x:float -> float
member DensityLn : x:float -> float
member Entropy : float
member InverseCumulativeDistribution : p:float -> float
member Maximum : float
member Mean : float
member Median : float
member Minimum : float
...
Full name: MathNet.Numerics.Distributions.LogNormal
--------------------
Distributions.LogNormal(mu: float, sigma: float) : unit
Distributions.LogNormal(mu: float, sigma: float, randomSource: System.Random) : unit
Full name: Optimization.variancePrior
Full name: Optimization.noisePrior
Full name: Optimization.prior
from Ariadne.Kernels
type Prior =
new : lengthscalePrior:LogNormal * signalVariancePrior:LogNormal * noiseVariancePrior:LogNormal -> Prior
member DensityLn : se:SquaredExp -> float
member ParamsDensityLn : parameters:float [] -> float
member Sample : unit -> SquaredExp
member LengthscalePrior : LogNormal
member NoiseVariancePrior : LogNormal
member SignalVariancePrior : LogNormal
Full name: Ariadne.Kernels.SquaredExp.Prior
--------------------
new : lengthscalePrior:Distributions.LogNormal * signalVariancePrior:Distributions.LogNormal * noiseVariancePrior:Distributions.LogNormal -> SquaredExp.Prior
Full name: Optimization.kernel
Full name: Optimization.gp
from Ariadne
Full name: Optimization.data
2006.0; 2007.0; 2008.0; 2009.0|];
-3.623076923; -2.063076923; -2.183076923; -1.813076923; 2.806923077;
4.386923077; 2.946923077; 0.7869230769|];
Full name: Optimization.newKernel1
module SquaredExp
from Ariadne.Optimization
--------------------
module SquaredExp
from Ariadne.Kernels
Full name: Ariadne.Optimization.SquaredExp.optimizeMetropolis
from Ariadne.Optimization
Full name: Ariadne.Optimization.MetropolisHastings.defaultSettings
Full name: Optimization.settings
Full name: Optimization.newKernel2
Full name: Ariadne.Optimization.SquaredExp.optimizeMetropolis
Full name: Optimization.gpInit
Full name: Optimization.gpOptim
Full name: Optimization.loglikInit
Full name: Optimization.loglikOptim
Full name: Microsoft.FSharp.Core.ExtraTopLevelOperators.printfn
Full name: Ariadne.GaussianProcess.plot
static member Area : data:seq<#value> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Labels:#seq<string> * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string -> GenericChart
static member Area : data:seq<#key * #value> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Labels:#seq<string> * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string -> GenericChart
static member Bar : data:seq<#value> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Labels:#seq<string> * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string -> GenericChart
static member Bar : data:seq<#key * #value> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Labels:#seq<string> * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string -> GenericChart
static member BoxPlotFromData : data:seq<#key * #seq<'a2>> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string * ?Percentile:int * ?ShowAverage:bool * ?ShowMedian:bool * ?ShowUnusualValues:bool * ?WhiskerPercentile:int -> GenericChart (requires 'a2 :> value)
static member BoxPlotFromStatistics : data:seq<#key * #value * #value * #value * #value * #value * #value> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Labels:#seq<string> * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string * ?Percentile:int * ?ShowAverage:bool * ?ShowMedian:bool * ?ShowUnusualValues:bool * ?WhiskerPercentile:int -> GenericChart
static member Bubble : data:seq<#value * #value> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Labels:#seq<string> * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string * ?BubbleMaxSize:int * ?BubbleMinSize:int * ?BubbleScaleMax:float * ?BubbleScaleMin:float * ?UseSizeForLabel:bool -> GenericChart
static member Bubble : data:seq<#key * #value * #value> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Labels:#seq<string> * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string * ?BubbleMaxSize:int * ?BubbleMinSize:int * ?BubbleScaleMax:float * ?BubbleScaleMin:float * ?UseSizeForLabel:bool -> GenericChart
static member Candlestick : data:seq<#value * #value * #value * #value> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Labels:#seq<string> * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string -> CandlestickChart
static member Candlestick : data:seq<#key * #value * #value * #value * #value> * ?Name:string * ?Title:string * ?Labels:#seq<string> * ?Color:Color * ?XTitle:string * ?YTitle:string -> CandlestickChart
...
Full name: FSharp.Charting.Chart
Full name: Optimization.gdSettings
from Ariadne.Optimization
Full name: Optimization.gradientFunction
Full name: Ariadne.Kernels.SquaredExp.fullGradient
Full name: Optimization.kernelGD
Full name: Ariadne.Optimization.gradientDescent
Full name: Ariadne.Kernels.SquaredExp.ofParameters
Full name: Optimization.gpGD

